

What a Difference an 'A' Makes!! 
This activity is designed to follow the Protein Synthesis Simulation where students have walked through the coding of a protein in order to understand how codons and anticodons work inside a living cell - a concrete example of a complex concept!! The exercise is considerably more abstract and will ultimately let you know who understands the mechanisms of this process.
I. DNA and RNA The model on the left side of the chart represents a segment of a single strand of DNA that has separated from its partner. Using the pictured strand as the original template, construct the following:
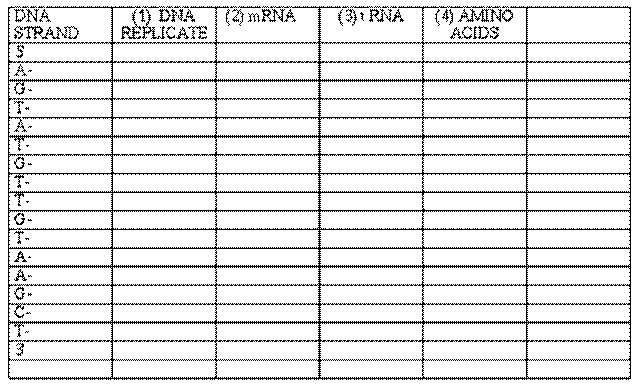
II. MUTATION
(A) Assume that the base in position 6 of the original DNA strand mutates to an "A." How will the sequence of 1,2,3, and 4 be affected?
(B) Suppose the base in position 2 gets shifted to position 16; how will the sequence of 1,2,3 and 4 (above) be affected?
(C) If the base in position 6 is changed to a "T," how will the sequence of 1,2,3 and 4 (above) be affected?
(D) Suppose the base in position 4 is removed. What happens to the strand? What kind of mutation is this?
|
U |
C |
A |
G |
|
U |
UUU Phenylalanine (Phe) |
UCU Serine (Ser) |
UAU Tyrosine (Tyr) |
UGU Cysteine (Cys) |
U |
UUC Phe |
UCC Ser |
UAC Tyr |
UGC Cys |
C |
|
UUA Leucine (Leu) |
UCA Ser |
UAA STOP |
UGA STOP |
A |
|
UUG Leu |
UCG Ser |
UAG STOP |
UGG Tryptophan (Trp) |
G |
|
C |
CUU Leucine (Leu) |
CCU Proline (Pro) |
CAU Histidine (His) |
CGU Arginine (Arg) |
U |
CUC Leu |
CCC Pro |
CAC His |
CGC Arg |
C |
|
CUA Leu |
CCA Pro |
CAA Glutamine (Gln) |
CGA Arg |
A |
|
CUG Leu |
CCG Pro |
CAG Gln |
CGG Arg |
G |
|
A |
AUU Isoleucine (Ile) |
ACU Threonine (Thr) |
AAU Asparagine (Asn) |
AGU Serine (Ser) |
U |
AUC Ile |
ACC Thr |
AAC Asn |
AGC Ser |
C |
|
AUA Ile |
ACA Thr |
AAA Lysine ( Lys) |
AGA Arginine (Arg) |
A |
|
AUG Methionine (Met) or START |
ACG Thr |
AAG Lys |
AGG Arg |
G |
|
G |
GUU Valine Val |
GCU Alanine ( Ala) |
GAU Aspartic acid (Asp) |
GGU Glycine (Gly) |
U |
GUC (Val) |
GCC Ala |
GAC Asp |
GGC Gly |
C |
|
GUA Val |
GCA Ala |
GAA Glutamic acid (Glu) |
GGA Gly |
A |
|
GUG Val |
GCG Ala |
GAG Glu |
GGG Gly |
G |
|
Protein Synthesis Activity
TACCCCTAGCAACTTGTTACAACGCGGAGTCAAACATCATATATAGTCGAACTCTTAATGACGTTG AAACATTTGGTTGTAAACACACCCAGGGTGGATCAACTCCGGAATATAAACCACACACCACTTTCT CCGAAAAAGATATGGGGCTTTCGTATC
The triplet codons above code for one of the smallest proteins in humans, the hormone insulin. The job of insulin is to remove excess sugar from your blood and take it to your liver where it can be converted into glycogen. (The gene for this protein is turned on shortly after one has completed a meal). In this activity, you are to complete the following:
1. Build the DNA molecule using the appropriate nucleotides/codons.
2. Transcribe/build an mRNA molecule that is complimentary to the DNA above.
3. Translate/determine the amino acid sequence.
4. Build the insulin molecule using the appropriate amino acids.
Helpful Web Sites:
http://nobel.scas.bcit.ca/resource/dna/station2.htm
http://gslc.genetics.utah.edu/units/basics/transcribe/